Box elder bugs, identifiable by their black and red markings, are common nuisances in households and gardens. This guide covers their identification, life cycle, habitats, and behavior. Understanding their impact is crucial for effective management. We’ll explore various control methods, including eco-friendly solutions for sustainable pest management. Learn everything you need to know to keep box elder bugs at bay.
What are Box Elder Bugs?
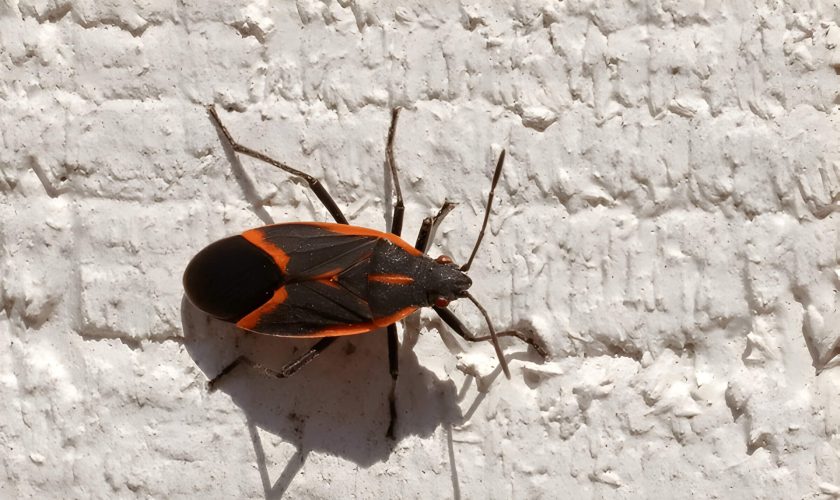
Box elder bugs, scientifically known as Boisea trivittata, are a common sight in North America, especially around box elder trees after which they are named. These insects can be identified by their distinct physical characteristics. Adult box elder bugs typically measure about half an inch in length and have a dark brown or black coloration with striking red or orange markings along their thorax and wings. Their elongated, oval-shaped bodies and six legs make them easily recognizable.
When it comes to box elder bug identification, it’s important to note that these bugs also possess prominent red eyes and two antennae. The nymphs, or immature stages of the bugs, are smaller in size but display bright red bodies which darken as they mature.
Understanding what box elder bugs look like is crucial for homeowners who may find these insects congregating on the sunny sides of buildings during cooler months. While generally harmless to humans and pets, their presence can be a nuisance due to their tendency to invade homes in large numbers seeking warmth. Recognizing these characteristics will help you manage and control any potential infestations effectively.
The Life Cycle of Box Elder Bugs
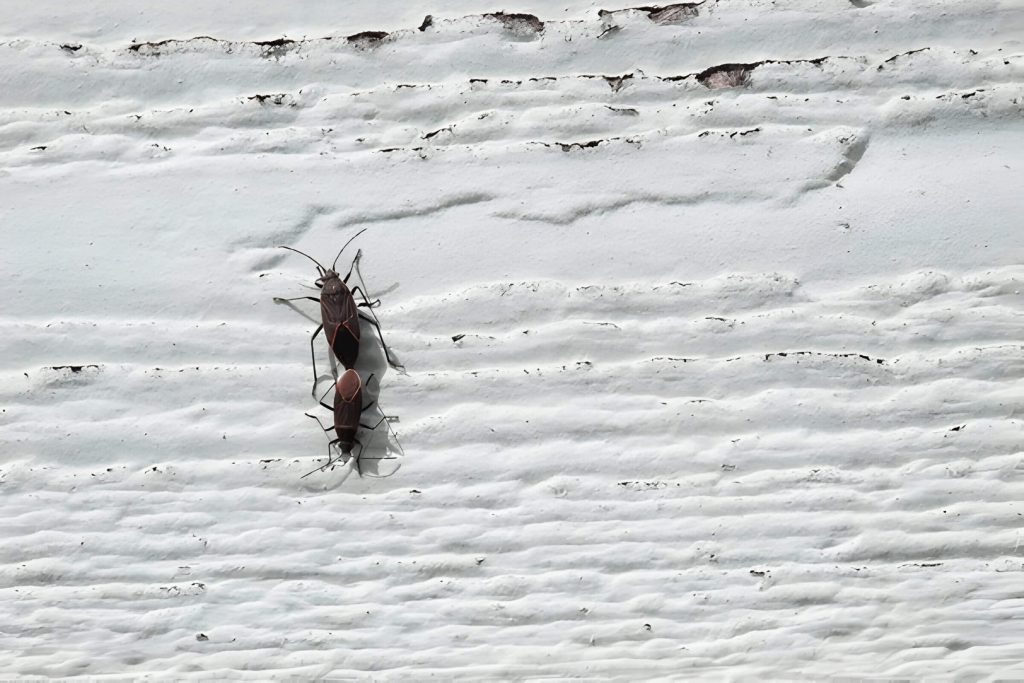

The life cycle of box elder bugs is a fascinating process that consists of several distinct stages. Understanding these stages can help in managing and controlling their populations. The box elder bug life cycle begins with the egg stage. Female box elder bugs lay their eggs in crevices of tree bark, typically on box elder trees, maple trees, or ash trees. These eggs are reddish-brown and hatch within a few days to weeks, depending on environmental conditions.
Once hatched, the nymph stage begins. Nymphs are small and bright red with black markings and go through several molts as they grow. Each molt brings them closer to their adult form, gradually developing wings and darkening in color.
The final stage is adulthood. Adult box elder bugs are about half an inch long with distinctive black bodies marked by red lines along the thorax and wings. At this stage, they become more mobile and seek out food sources such as seeds from box elders or other trees.
As for longevity, how long do box elder bugs live? Typically, their lifespan ranges from a few months to a year depending on environmental factors like temperature and food availability.
Understanding the stages of the box elder bug life cycle can be crucial for effective pest management strategies. By targeting specific stages like eggs or nymphs, it’s possible to reduce their numbers before they reach adulthood and reproduce further.
Common Habitats and Behavior of Box Elder Bugs
Box elder bugs are commonly found in regions where box elder trees, maple trees, and ash trees are prevalent. These insects thrive in areas with a moderate climate, making them widespread across the United States. The primary box elder bug habitat includes tree bark, leaves, and seeds of their preferred host plants. During the warmer months, they can often be seen congregating on the sunny sides of trees and buildings.
As for their behavior patterns, box elder bugs exhibit distinct seasonal habits. In spring and summer, they feed on the sap from leaves, flowers, and developing seeds of host trees. This feeding does not typically cause significant damage to healthy trees but can be a nuisance when populations are high. As temperatures drop in autumn, these bugs seek shelter to overwinter. They often find refuge in cracks and crevices of buildings or under loose bark.
Understanding where box elder bugs live and their behavior patterns is crucial for managing their presence around homes and gardens. By identifying potential habitats and seasonal behaviors, homeowners can take proactive measures to prevent infestations before they become problematic.
The Impact of Box Elder Bugs on Homes and Gardens
Box elder bugs, often found in large numbers, can become a significant nuisance for homeowners and gardeners alike. These insects are typically attracted to box elder trees, but they do not limit themselves to these alone; they also target maple and ash trees. The presence of box elder bugs in the house usually spikes during the fall when they seek warm places to overwinter.
In gardens, box elder bugs are considered pests primarily because of their feeding habits. They feed on the leaves, flowers, and seed pods of various plants. Although their feeding does not typically kill plants, it can cause noticeable damage such as leaf discoloration and deformities which can affect the overall aesthetic appeal of your garden.
When it comes to homes, while box elder bugs do not cause structural damage or pose health risks to humans or pets, their sheer numbers can be overwhelming. They tend to congregate in sunny areas on exterior walls before finding ways into homes through cracks and crevices. Once inside, they can be difficult to remove and may leave behind stains from their excrement on curtains and walls.
Understanding how these garden pests operate is crucial for effective management. Sealing entry points around your home and maintaining a clean garden by removing debris can significantly reduce their numbers. For severe infestations, professional pest control services may be necessary to manage the damage caused by box elder bugs effectively.
Effective Methods to Control and Prevent Box Elder Bug Infestations
Box elder bugs can be a nuisance, especially during the fall when they seek shelter inside homes to escape the cold. Understanding effective methods to control and prevent these pests is crucial for maintaining a bug-free environment.
One of the primary pest control methods for box elders involves sealing entry points. Inspect your home for cracks, gaps, and holes around windows, doors, and foundations. Use caulk or weatherstripping to seal these potential entryways. This preventive measure not only helps keep box elder bugs out but also improves overall energy efficiency.
Another effective strategy is to reduce their habitat by managing vegetation around your home. Box elder bugs are attracted to box elder trees and other seed-bearing plants. Consider removing female box elder trees from your property or at least trimming back branches that are close to your house.
For those wondering how to get rid of box elders bugs once they’ve entered the home, vacuuming is a practical solution. Use a vacuum cleaner with a hose attachment to suck up any visible bugs. Dispose of the vacuum bag immediately to prevent them from escaping back into your living space.
Insecticides can also be used as a last resort but should be applied with caution. Focus on exterior applications around windowsills, door frames, and other entry points where box elder bugs congregate.
By combining these preventive measures with timely interventions, you can effectively control and prevent box elder bug infestations in your home.
Naturally Deterring Box Elder Bugs
Box elder bugs, though relatively harmless, can become quite the nuisance when they invade homes and gardens in large numbers. Fortunately, there are several natural pest control methods for box elders that are both effective and eco-friendly. By adopting these organic solutions for pest management, you can maintain a healthy environment while keeping these pests at bay.
One of the most straightforward eco-friendly ways to deter pests like box elder bugs is to seal entry points around your home. Check for gaps around windows, doors, and foundations where these insects might enter. Using caulk or weather stripping can effectively block their access.
Another natural method involves using essential oils known for their insect-repelling properties. Spraying a mixture of water and essential oils such as tea tree oil or lavender around potential entry points can discourage box elder bugs from entering your space.
Maintaining a clean yard is also crucial in natural pest control for box elders. Regularly remove debris such as fallen leaves and branches where these bugs might congregate. Additionally, planting certain types of flowers like marigolds or chrysanthemums can naturally repel box elder bugs due to their strong scents.
Finally, consider introducing natural predators into your garden. Birds and beneficial insects like ladybugs feed on box elder bugs and help keep their population under control without the need for chemical interventions.
By utilizing these eco-friendly solutions, you not only manage the presence of box elder bugs but also contribute to a healthier ecosystem overall.